Systeme.io vs ClickFunnels (2026): Which Funnel Builder is Best for Entrepreneurs?

Sales funnels guide a prospect from awareness to action. Today’s online entrepreneurs use drag-and-drop funnel builders to create these pipelines. ClickFunnels is a veteran all-in-one marketing platform for funnels, email, membership sites and more. Systeme.io is a newer all-in-one business platform that also covers funnels, email marketing, courses, websites and even an affiliate program. Crucially, ClickFunnels plans start around $97/month, whereas Systeme.io even offers a robust free forever plan (with up to 3 funnels and 2,000 contacts). In this 2026 comparison we’ll break down features, pricing, pros/cons and use cases to help beginners and solopreneurs decide which is the better funnel builder. What Is Systeme.io? Systeme.io is positioned as a simple, all-in-one marketing software for small businesses and creators. Founded by Aurelien Amacker, it was built to combine funnels, email marketing, courses and more in one place (avoiding multiple tools). The platform includes a drag-and-drop funnel/website builder and tools to send unlimited automated emails, host courses, set up blogs, and manage an affiliate program. Beginners find its clean interface very user-friendly: you can build pages with clicks and code-free templates. Systeme.io even offers unlimited emailing, file storage, students and no transaction fees on all plans – features that some competitors charge extra for. In practice, most users find they can run an online course, capture leads, and sell products all from this single dashboard. As one reviewer noted, “Systeme.io covers almost everything most beginners need” and is “much cheaper” than alternatives. The free plan alone lets you test the core features: you get 3 funnels (15 pages each), unlimited emails, 2,000 contacts, 1 course site and even built-in affiliate management. That makes it easy to try out before upgrading. Systeme.io’s Pricing is very affordable. In 2026 it offers four tiers: Free ($0), Startup ($17/mo), Webinar ($47/mo), and Unlimited ($97/mo). Each paid tier adds more funnels, contacts and automation rules (for example, Startup includes 10 funnels and 5,000 contacts). Annual billing gives two months free (so Startup is ~$14.16/mo billed yearly). For most small businesses, even the Startup plan provides all necessary tools, and it’s easy to upgrade as you grow. In short, systeme.io delivers an all-in-one solution at an affordable price. Get started with the free Systeme.io plan What Is ClickFunnels? ClickFunnels is one of the original all-in-one funnel builders, co-founded by Russell Brunson. It too combines a funnel/page builder, email automation, membership sites and sales tools. The platform revolutionized online marketing by letting users build entire sales funnels without coding or hiring designers. In 2026 ClickFunnels 2.0 continues that legacy. It includes a powerful drag-and-drop funnel editor with dozens of high-converting templates and built-in A/B testing. Key ClickFunnels features include: In short, ClickFunnels aims to give you “everything you need to launch and grow an online business” in one place. It’s very feature-rich, though that also means it can feel more complex. Notably, ClickFunnels does limit some things by plan: the standard (Launch) plan includes 3 domains and limited funnels/pages, while the Funnel Hacker plan ($297) unlocks unlimited funnels and advanced tools. However, even the Launch plan includes key features like unlimited funnels, AI tools and custom domains. Comparing Features and Pricing Let’s compare the two across key factors: Pros and Cons ClickFunnels– Pros: All-in-one powerhouse – funnels, CRM, emails, courses, and more in one platform. Easy drag-and-drop funnel builder with A/B testing, plus built-in upsells/downsells and optimization tools. Extensive resources and community (training, templates, integrations).– Cons: High Cost: Plans start at $97/mo and go much higher. Learning Curve: The multitude of features can overwhelm beginners. Performance: Some users report slower page load times and occasional glitches. Limited Design Freedom: Even with many templates, fully custom designs can be tricky without a developer. Systeme.io– Pros: Extremely affordable, with a generous free plan and low-priced paid tiers. Truly all-in-one: funnels, emails, courses, affiliate program, blogs – no need to juggle multiple apps. Very beginner-friendly interface and simple setup. Built-in automation and affiliate tracking save time and tools. No transaction fees and unlimited emails/storage on all plans.– Cons: Basic Templates: Fewer fancy page designs; some templates are more simple. Feature Depth: Lacks some advanced course/membership features and detailed analytics of specialized platforms. Email/SEO Tools: Functional but more limited (basic editor and SEO settings). Overall, serious marketers may find it less flexible than ClickFunnels. Who Should Use Which In short, Systeme.io wins for affordability and ease, especially if you want to focus on results without tech headaches. ClickFunnels wins for advanced funnel customization, at the cost of complexity and price. Conclusion & Recommendation Both Systeme.io and ClickFunnels can build high-converting funnels, but they suit different entrepreneurs. ClickFunnels is powerful and feature-packed, but it’s significantly more expensive and has a steeper learning curve. For most small businesses, startups and affiliates, Systeme.io is the smarter choice in 2026. You get an all-in-one marketing platform — funnels, email, courses, etc. — at a fraction of the price. If budget is tight or you’re just getting started, start with Systeme.io’s free plan. It lets you launch funnels, send unlimited emails, and even run an affiliate program with no credit card required. Once you see the results, you can upgrade to a paid plan as needed. In our view, systeme.io offers the best value for small entrepreneurs. Ready to build your first funnel? Sign up for Systeme.io’s free account today and experience an affordable, beginner-friendly funnel builder that won’t break the bank. [sources- systeme.io]. Get started with the free Systeme.io plan
American Eagle Stock Shoots Up: How Sydney Sweeney & Travis Kelce Turned Fashion Into Market Momentum
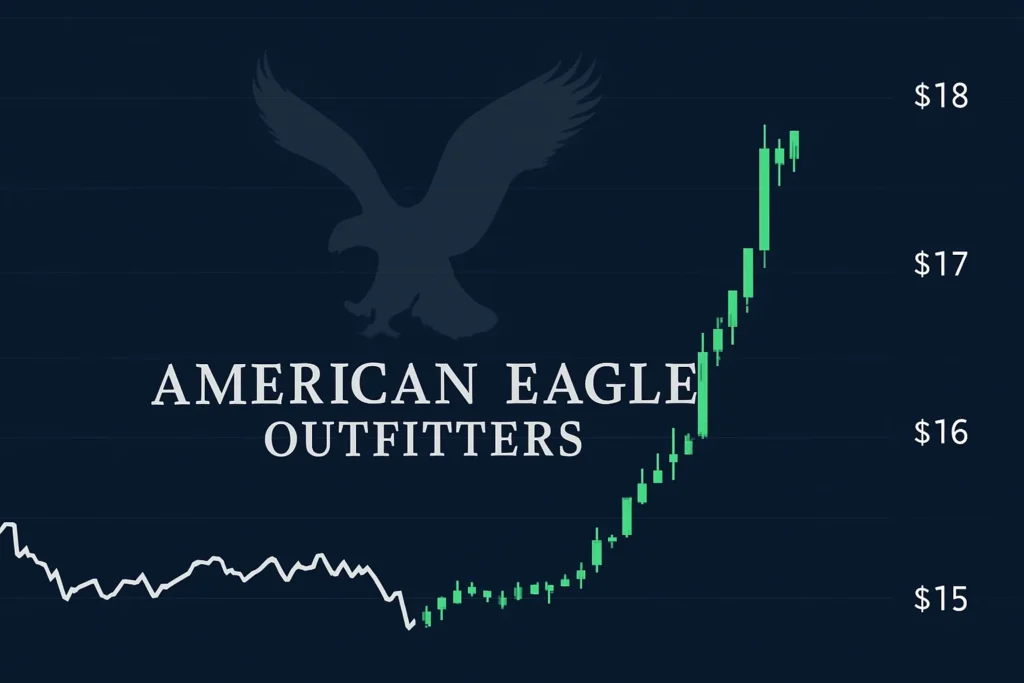
American Eagle Outfitters (NYSE: AEO) isn’t usually the center of Wall Street chatter. Known mostly for its mall presence and classic denim, the brand suddenly experienced something extraordinary: its stock surged over 30%—and the spark came directly from two big names: Sydney Sweeney and Travis Kelce. The Celebrity Factor: Beyond Just Glamour American Eagle’s new denim campaign starred Sydney Sweeney, famed for Euphoria, and Travis Kelce, the NFL star turned cultural household name due to his relationship with Taylor Swift. This pairing didn’t just boost follower counts—it sparked major financial interest too. As Reuters reported, the campaign “generated unprecedented new customer acquisition” and helped American Eagle ride high in a cautious spending climate. What Really Caused the Stock to Soar Once the campaign dropped, the investor community responded quickly. According to Reuters, the 33% stock jump was fueled by the ad’s viral reach and powerful customer turnout. The Times of India also highlighted the surge, noting a 25% rise in stock price alongside record-breaking customer engagement, all directly tied to the celebrity-driven strategy.What Wall Street Is Watching The campaign didn’t just spark social buzz; it turned into real-world results. AP News observed that despite initial backlash, the campaign translated into “record-breaking new customer acquisition and brand awareness.” Foot traffic improved, and the company adjusted its sales outlook positively. Further, Reuters confirmed that American Eagle now expects better-than-expected comparable-store sales heading into fall, citing the impact of the Sweeney and Kelce campaigns. Celebrity Influence Meets Market Psychology This isn’t just marketing—it’s a powerful synergy of celebrity culture, social media, and market psychology: Should Investors Buy the Hype? For day traders, the rally offered quick gains. But long-term investors must weigh: Still, if American Eagle keeps innovating with culturally smart campaigns, this stock may prove to be more than a one-time pop. Bottom Line American Eagle’s latest rally proves that culture and commerce can be powerful allies. In 2025, Sydney Sweeney and Travis Kelce didn’t just sell denim—they moved markets. As investors rethink what drives growth, the key takeaway is clear: Wall Street is watching Mall Street, and sometimes a viral campaign is the smartest financial play of all. This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial advice. Always perform your own due diligence or consult a licensed advisor before making investment decisions.
Private Credit: A Comprehensive Guide for Businesses and Investors

Private credit (also called private debt or direct lending) refers to loans made by non‐bank institutions – such as private equity firms, business development companies (BDCs), or alternative asset managers – directly to companies. Unlike public bonds or syndicated bank loans, these loans are negotiated privately and usually held to maturity by the lender. The asset class has exploded in size over the past decade: global private credit assets under management (AUM) have grown from a few hundred billion in the early 2010s to over $1.6 trillion by 2023 (sources – ubs.com). In the U.S. alone, private credit volumes swelled from just $46 billion in 2000 to roughly $1 trillion by 2023. This growth reflects both strong investor demand for higher-yielding, alternative income and borrowers’ appetite for flexible financing when traditional bank loans are constrained. Key features of private credit: loans are typically floating-rate (indexed to benchmarks like SOFR), structured with rich covenants, and aimed at mid-sized or leveraged companies. Investors commit long-term capital, so private credit funds don’t rely on retail deposits – this makes private credit more “illiquid” and justifies higher interest rates. For example, private loans often carry spreads of 200–400 basis points above public rates to compensate for illiquidity. These deals tend to be covenant-heavy (to protect lenders), in contrast to looser “covenant-lite” public loans. In practice, a typical private loan might be $10–250 million for 3–7 years, although sizes have risen: recent data show the average private credit loan exceeded $80 million by 2022 – much larger than loans made by local banks. Why Private Credit Is Growing Private credit’s rise is driven by several factors. After the 2008 financial crisis, banks faced tighter regulation and capital rules. At the same time, bond yields plunged to record lows. Institutional investors (pension funds, endowments, insurance companies, family offices) seeking higher income turned to alternative debt. “With interest rates near zero, returns on government and corporate bonds were unattractive,” notes Brookings: this “reach for yield” pushed capital into private credit funds. In the U.S. alone, 28% of private credit fund capital comes from pension funds, 21% from endowments, and 19% from wealthy families. Businesses also find private credit appealing. Compared to banks, private lenders often execute deals faster and customize terms. Borrowers benefit from upfront pricing, tailored covenants, and flexible amortization schedules. As Brookings observes, private funds advertise “their ability to provide loans to businesses quickly, on flexible terms, and with pricing available to borrowers upfront”. This is especially valuable for companies that are too small, unrated, or niche for public debt markets. These drivers have combined to make private credit one of the fastest-growing corners of finance. As PwC reports, “the rise of the private credit ecosystem is causing a fundamental realignment in the debt value chain in capital markets”. How Private Credit Works (vs. Traditional Loans) Private credit is fundamentally non-bank lending. A firm (often backed by a private equity sponsor or seeking an acquisition) negotiates a loan directly with a private lender. Unlike a bank, the lender usually commits its own or investor capital and holds the loan on its balance sheet. There is no public issuance or broad syndication; indeed, private loans typically do not trade in liquid markets. Key differences from traditional bank loans: Each private credit deal is negotiated case-by-case. Lenders may combine senior debt, subordinated debt, or even mezzanine tranches in one package. They price the loan to include a substantial illiquidity premium – for example, spreads up to 400 basis points above bank benchmarks have been common. In exchange, borrowers get quick execution and often more flexible amortization or extension features than bank debt. Figure: The private credit market has grown rapidly. Global private debt AUM has more than quadrupled since 2015, reaching roughly $1.6–1.8 trillion by 2024. Charts like this (from UBS Asset Management) illustrate the surge. Benefits of Private Credit Private credit offers advantages for both borrowers and investors: Risks and Concerns While the private credit market has grown rapidly, it is not without risks: Regulatory watchers are paying attention. For example, the U.K. Bank of England recently highlighted that private credit had quadrupled since 2015 (to an estimated $1.8T by 2024) and noted much of that came in a low-rate era. Policymakers ask whether, in a downturn, private credit could amplify shocks. As the PwC report warns, the sector’s much larger scale today means “if defaults rise… there could be a systemic feedback loop” to the broader economy. Private Credit Around the World Private credit is a global market, though with regional differences. The U.S. remains the largest by far – roughly 40% of global private credit funds focus on U.S. companies. Europe is the second-biggest market, driven by pension capital and an active mid-market. Asian private credit is still nascent but growing: JPMorgan recently noted APAC private credit deals total roughly $200 billion annually (versus a $1.5T public debt market), implying big room to expand(sources- reuters.com). Figure: Deal size distribution in private credit. Larger and mid-size transactions now make up a significant portion of direct lending. UBS data (2024) show that the private credit market is accommodating increasingly big loans. This reflects the trend that “private credit loans have become larger” and more similar to big syndicated loans. Case Studies and Examples Practical examples illustrate private credit’s role: Big industry consolidations also underscore private credit’s momentum. In late 2024 BlackRock agreed to acquire HPS Investment Partners for $12 billion(sources– alternativecreditinvestor.com) (giving BlackRock a top-tier credit business). Similarly, Ares Management bought GLP Capital Partners for $3.7 billion (adding $44 billion AUM)(sources – alternativecreditinvestor.com). Firms like Blue Owl, Stonepeak, and others have snapped up credit managers worldwide. These moves highlight how financial institutions are investing heavily to build out private lending platforms, anticipating continued demand. Future Outlook All signs point to further growth. BlackRock projects private credit will exceed $3.5 trillion by 2028, potentially surpassing today’s combined leveraged loan and high-yield bond markets. The “addressable market” is enormous – some analyses even cite figures like $30 trillion when counting non-investment grade borrowing globally. Key factors for the coming years include: In summary, private credit is much more than a niche today. It has become a mainstream source of capital for companies worldwide. Borrowers appreciate its speed and flexibility, while investors value its yields.
How Blockchain is Transforming the IT Industry: It Could Make or Break Your Business

Introduction what is Blockchain technology? Blockchain technology is transforming industries globally. It is a digital, decentralized ledger that maintains a record of every transaction on a network of computers. Blockchain is most famous for being the underpinning for digital currencies like Bitcoin, but it has a variety of other potential applications. In this article, we examine how blockchain technology is transforming our understanding of digital inflow/outflow and how it’s being utilized to transform a variety of industries. From Bitcoin to Business: How Did Blockchain Enter the IT Industry? Satoshi Nakamoto unveiled blockchain technology in 2008 as the basis for Bitcoin, allowing direct transactions without the help of banks. Through autonomous verification, it acts as a public ledger noting Bitcoin transactions and hence promotes trust and transparency. Developers developed alternate cryptocurrencies (altcoins) like Ethereum and Litecoin as Bitcoin grew in popularity. Introduced in 2015, Ethereum brought smart contracts, which enable decentralized applications (dApps) by automating agreements. This signaled a change from blockchain as only a payment method to a platform for building autonomous systems. Many sectors started to see blockchain’s wider potential by 2016–2017, especially for data integrity, supply chain openness, digital identity management, and safe information sharing. This interest resulted in the acceptance of corporate blockchain technologies. Emergent new blockchain systems stressed permissioned networks, quicker transactions, and data privacy above all else. Hyperledger Fabric, R3 Corda, and Quorum among others are examples. Microsoft and Amazon provide Blockchain-as-a-Service (BaaS) so that businesses may quickly create blockchain systems. Blockchain is gaining traction in sectors including banking, logistics, healthcare, and government. Blockchain is developing alongside artificial intelligence, IoT, and cloud computing, thereby creating the way for smart cities and distributed finance. Why is it important to discuss blockchain’s role in IT transformation? Amidst continuous digital innovation, the text emphasizes the need of blockchain in changing the IT sector. Often centralized and sensitive to cyber threats, data loss, and scaling problems, conventional IT systems’ main difficulties are addressed by blockchain. It inspires IT leaders to reevaluate outdated models and embrace contemporary infrastructure by providing a decentralized, safe environment with data immutability, cryptographic security, and consensus mechanisms. Furthermore, blockchain alters the character of data ownership and trust. It builds distrust-free systems where code rather than people holds responsibility, rather than depending on middlemen like banks or servers. This change gives users more control over their information by affecting how identity and data governance are handled. By combining with technologies like artificial intelligence, the internet of things (IoT), and cloud computing, blockchain also powers next-generation applications and allows for inventions like smart cities and decentralized finance (DeFi). Without knowing the function of blockchains, IT experts risk trailing behind. Many companies, including some of the biggest ones, are aggressively using blockchain for uses like safe transactions and supply chain management, therefore pointing to its growing strategic value for IT experts to stay informed and competitive. Finally, by generating demand for jobs like blockchain developers and security architects, blockchain is changing job titles and skill sets inside IT. Its features motivate invention, efficiency, and adherence, therefore enabling IT teams to best utilize their systems in ways that legacy technologies cannot. Public vs Private Blockchain Use in IT Because of its potential for data integrity, security, transparency, decentralization, and promise in the IT industry, blockchain technology is fast becoming quite popular. Not all blockchains are alike, though. Depending on the use case, businesses may decide among public and private blockchain systems each with its own advantages and downsides. What is a Public Blockchain? A public blockchain is a decentralized, open network where anyone can participate, read, write, or validate data. It runs without central control or authorization layer. IT Benefit: Ideal for solutions requiring maximum transparency, global access, and censorship resistance. What is a Private Blockchain? Access on a private blockchain—also known as a permissioned blockchain—is restricted to certain participants. It is sometimes managed by one company or group of companies. IT Benefit: Ideal for enterprises that require control, performance, and confidentiality while still gaining the benefits of blockchain. Crucial Ways Blockchain is Revolutionizing the IT Industry Once only applicable to bitcoin, blockchain technology now reaches far beyond that. It is becoming a fundamental technology for contemporary IT systems, assisting companies to simplify processes, improve security, and promote innovation. Decentralization, openness, and automation on blockchain are changing the whole IT infrastructure and how companies manage data, identity, and trust. 1. Improving Data Integrity and Cybersecurity Data in conventional IT systems is usually kept in centralized databases, therefore rendering it an ideal target for data breaches, cyberattacks, and illegal access.By way of blockchain counters these hazards: • Decentralization distributes data across a network, reducing attack risk.• Immutability prevents alteration or deletion of information.• Cryptographic security protects records with hashing.• Guardtime uses blockchain for data integrity in government and healthcare. 2. Automating IT Operations with Smart Contracts A smart contract is code on the blockchain that executes actions automatically when conditions are met, removing manual processes and third-party validation. It automates workflows, reduces errors and fraud, and enables trustless automation. Example: a cloud service provider automates resource access after payment verification. 3. Enabling Decentralized Applications (dApps) Decentralized applications (dApps) operate on blockchain networks, offering resilience, transparency, and censorship resistance. They enable independent development, reducing costs and enhancing security, exemplified by decentralized code-sharing tools. example: Open-source collaboration tools like GitHub alternatives are emerging as dApps to allow decentralized code sharing. 4. Revolutionizing Data Management and Access Control Blockchain helps manage large data volumes by synchronizing data in real-time, controlling access with digital identities, and creating tamper-proof audit trails. Example: In multi-cloud environments, IT teams can use blockchain to maintain a consistent data version across platforms, ensuring that all updates are recorded securely. 5. Improving Transparency and Auditability Blockchain’s transparent ledger permanently records transactions, timestamps them, and allows public verification. This gives IT professionals end-to-end visibility, accountability in development, and simplifies auditing. Financial institutions utilize it for efficient tracking and auditing of IT operations, decreasing manual review time and costs. 6. Driving Innovation Through
Snapchat Company – Latest Financial Analysis & Company Overview

Introduction More than a venue for vanishing communications and strange filters, Snapchat is the focus of Snap Inc., a global camera and social tech company always changing. Snapchat company has overturned the way we visually interact since its start in 2011. Snap Inc., meanwhile, has been on a rollercoaster of invention, expansion, contention, and volatile revenues. From features and funding to market trends and future aims, let’s break down everything about Snapchat in 2025. Company Overview Snap Inc. – The Parent Company Snapchat Company is owned by Snap Inc., a publicly traded company listed on the Snapchat is owned by publicly held company Snap Inc., which is listed on the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE) under the ticker symbol SNAP. Snap Inc. is headquartered in Santa Monica, California, and positions itself as a camera company with a mission rooted in helping people live in the moment and share their stories. Founders and Early History It was invented by Evan Spiegel, Bobby Murphy, and Reggie Brown when they were all at Stanford University and first released as “Picaboo.” The ephemeral messaging focus of the app was a quick hit, and it grew exponentially in the space of a few years. Major Products and Services Business Model How Snapchat Makes Money Snapchat has diversified its sources of income over the years but continues to rely heavily on advertisement. Advertising Revenue Snap’s largest revenue source comes from Snap Ads, AR Lenses for Brands, and placements for Discover content. The platform possesses advanced audience targeting and visual storytelling capabilities that are ideal for advertisers. Subscription Revenue – Snapchat+ In 2022, Snap introduced Snapchat+, a subscription that offers early feature access, unique icons, and tools. Through 2025, this contributes a growing percentage to recurring revenue. AR Lenses and Spotlight Monetization Snapchat monetizes via: Recent Product Updates (2025) Home Safe Feature Snap introduced Home Safe back in July 2025, which allows friends to send an automatic alert to friends as they arrive home safely with the assistance of Snap Map. The safety feature was embraced, particularly by teenagers. Reversal of “Simple Snapchat” Redesign Snap abandoned its minimalist redesign idea after it emerged through testing that user engagement plummeted. Over 1 million North American users lost access due to the changes, prompting the company to retain the proven five-tab interface. Spotlight and AR Innovation Snap has doubled down on AR and its TikTok-like Spotlight feed, both of which it has made more advertiser- and creator-friendly with new monetization options and real-time measurement. Financial Performance Year-Over-Year Revenue Analysis North American revenue is the largest and most robust segment, but Snap also is seeing solid growth in Europe and Asia-Pacific. Operating Expenses and Profit Levels nap’s cost of operations decreased modestly due to layoffs and a leaner product pipeline. R&D remains high, however, as the company invests heavily in AR, AI, and machine learning. Here is the Official Annual Report Stock Market Insights Snap Inc. Stock Performances (YTD) As of July 2025, the stock of Snap Inc. is trading at approximately $13.42, rebounding modestly after a Q1 dip. Healthy user growth and better ad revenue performance are credited by analysts for the rebound. Analyst Forecasts and Predictions Analysts project moderate growth with a target price of $16–$18 in the next 12 months. Shareholder Reactions Investors provided a sign of fresh optimism, particularly following the reversal of unpopular design modifications and inclusion of user-led features. User Statistics and Active Daily Users Snapchat has 422 million Daily Active Users as of mid-2025. Most users open the app over 30 times a day, with the majority of them using chat, filters, and Stories. Gen Z and Millennial Use Snap remains a Gen Z favorite. In the U.S., over 70% of 13–24-year-olds use Snapchat regularly, making it a vital channel for youth-oriented marketing. Regional Breakdown Advertising and Partnerships Large Brand Partnerships Snap has partnered with Nike, Samsung, and Pepsi, among countless others, on high-ROI AR experiences that blend immersive stories with spontaneous user interaction. Self-Serve Ad Platform Snap Ads Manager enables any-sized companies to manage campaigns. Its targeting and analytics features are being likened to Facebook Ads in terms of strength. Performance Indicators Ad engagement and ROI are further enhanced. AR campaigns deliver 3x the engagement of traditional mobile display ads, according to internal measurement. Competitive Landscape Competing Platforms (Instagram, TikTok) Snap competes with YouTube Shorts, Instagram, and TikTok, with a focus on short-form video and AR. Distinctive Features Strategic Positioning Snap’s strategy is to double down on AR, target Gen Z, and provide creators with more monetization than its rivals. Leadership & Management Evan Spiegel – CEO Evan Spiegel remains the CEO. His innovative approach—albeit at times risky—has kept Snap current and at the forefront. Executive Management and Strategy The response is informed by experienced tech veterans across product, engineering, and operations. 2025 priorities: User retention, profitable growth, and AR-first experiences. Vision for the Future Snap wants to be the go-to AR platform for creators and advertisers while retaining its fundamental nature as a secure and innovative place for teens. Challenges and Controversies Antitrust References with Meta It was revealed in Meta’s antitrust trial in July 2025 that Mark Zuckerberg made a bid to buy Snapchat in 2013, which was rejected. It was again brought to court to establish anti-competitive conduct. Privacy Concerns As with all social media, Snapchat is under pressure from privacy, particularly from European regulators User Backlash on Redesign he failed “Simple Snapchat” redesign damaged trust. But Snap’s quick recovery repaired its reputation. Innovations & Future Plans AI Integration Snap is integrating AI to enhance Lens personalization, filter recommendations, and ad targeting. AR & VR Development Snapchat’s next-gen AR glasses and 3D lenses aim to blur the line between digital and real-world storytelling. Creator Monetization Expansion Snap is developing creator hubs, analytics dashboards, and sponsorship tools to attract influencers. Conclusion Snapchat business and parent company Snap Inc. are riding the choppy social media waters with a combination of innovation and grit. Against the backdrop of user anger and fierce competition, Snap’s emphasis on AR, AI, and user-friendly design is reaping dividends. On the financial front, the business is steadying, with better margins and greater investor confidence. As we navigate 2025, Snap seems set for long-term growth, fueled by technology, transparency, and a passion for creativity. FAQs 1. Who controls Snap corporate? Snap Inc., a public company co-founded by Evan Spiegel, owns Snapchat. 2. Snapchat’s revenue sources are: Snapchat’s revenue derives primarily from advertising, subscriptions (Snapchat+), and creative monetization instruments. 3. Snapchat 2025 offers what? Among the more noteworthy changes are Spotlight’s Monetization Tools, AR innovation, and the Home Safe capability. 4. Snapchat is profitable? Snap is reducing losses and approaching profitability. Better margins and lower net loss were seen in Q2 2025. Snapchat has around what total users worldwide? As of mid-2025, Snapchat has around 422 million Daily Active Users, with strong growth in Asia and Europe.
Stimulus Check 2025: What’s Real, What’s Rumor, and What’s Already Paid

Stimulus checks remain a hot topic in 2025 as millions of Americans seek clarity on upcoming payments. This comprehensive guide explains: We back all insights with official IRS releases and trusted financial news sources to keep you informed and protected What’s Real in 2025? 1. Unclaimed Recovery Rebate Credit (2021 Stimulus) Deadline:Individuals needed to file their 2021 tax return by April 15, 2025 to claim it. This window has now closed. Sources: (IRS.gov, Kiplinger, Benefits.com) Historical Stimulus Timeline (2020–2025) Here’s a quick overview of past stimulus payments to understand the context: Date Amount Details April 2020 $1,200 CARES Act (EIP 1) Dec 2020 – Jan 2021 $600 COVID Relief Package (EIP 2) March 2021 $1,400 American Rescue Plan (EIP 3) Jan 2025 Up to $1,400 Unclaimed 2021 Recovery Rebate Credit What’s Rumor in 2025?1. $1,700 Check in July 2025 Source: June Lake Trails Fact Check 2. $2,000–$2,500 “Fourth Stimulus” Source: DotDataScience 3. $5,000 “DOGE Dividend” Source: Houston Chronicle Why No New Federal Stimulus in 2025? Despite public demand, no new federal stimulus checks have been approved in 2025 due to: Sources: IRS.gov, Befluent in Finance State-Level Stimulus and Relief Programs While federal stimulus is paused, several states continue aid programs in 2025: State Program Amount Alaska Permanent Fund Dividend $1,312 (avg) California Middle-Class Tax Refund $200 – $1,050 New Mexico Rebates for tax filers Up to $500 Check your state tax agency website for updated eligibility and payment dates. How to Protect Yourself Against Stimulus Scams With high misinformation, remember: What’s Already Paid? Sources: IRS.gov, Finger Lakes 1 Quick Comparison Table Claim Status Details $1,400 Recovery Rebate Credit Real Paid to eligible filers by Jan 2025. $1,700 or $2,000 New Checks Rumor No IRS or Treasury confirmation. $5,000 DOGE Dividend Speculative No legal mandate or Congressional approval. ❓ Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) 1. Will there be a fourth stimulus check in 2025? No. As of July 2025, no new federal stimulus payments are approved. 2. Are SSI and SSDI recipients getting any stimulus this year? No specific federal stimulus, but state benefits and cost-of-living adjustments (COLA) continue as scheduled. 3. Can I still claim the 2021 Recovery Rebate Credit? The deadline was April 15, 2025. Late claims are no longer accepted. 4. How do I check if I received my payment? Use the IRS “Get My Payment” tool or check your 2021 tax transcript online. 5. What should I do if I see ads promising a $2,500 check? These are misleading. Always verify through IRS.gov or trusted financial news. 6. Will the DOGE Dividend become law? Currently, it is a speculative proposal without legal approval. 7. Where can I find state-specific relief programs? Visit your state’s Department of Revenue or Taxation website for official updates. Final Thoughts What’s real: The $1,400 Recovery Rebate Credit sent in early 2025.What’s rumor: Claims of new $1,700 or $2,000 federal checks remain unfounded.Already paid: All official COVID-era stimulus payments have been processed. 👉 Stay updated:
Top Cyber Security Insurance Companies: The Complete 2025 Guide

In today’s digital-first world, cybersecurity risks have become a daily concern for every business – from small startups to global enterprises. As data breaches, ransomware, and sophisticated hacking attempts continue to rise, companies are turning towards cybersecurity insurance companies for financial protection and peace of mind. To help you navigate this complex landscape, understanding the role of cyber security insurance companies is crucial. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about cyber insurance providers, how they work, what they cover, and the best companies to consider in 2025. Table of Contents Introduction to Cyber Security Insurance Cyber security insurance, often called cyber liability insurance, is a specialised policy designed to protect businesses against internet-based risks and data breaches. These policies cover costs related to recovery, legal liability, customer notification, and reputational damage after an attack. With the frequency and severity of cyber attacks increasing, many industries now treat cyber insurance as essential rather than optional. Why Cyber Insurance is Critical in 2025 In 2025, the global business landscape has become more digitalised than ever before. From remote work systems to cloud integrations and AI-driven operations, companies rely heavily on technology. This dependence exposes them to threats like: A single breach can cost millions in recovery and penalties, making cyber insurance a strategic investment rather than an expense. What Does Cyber Security Insurance Cover? While coverage differs among providers, most cyber insurance policies include: Understanding these coverage areas ensures you choose a policy that protects your business comprehensively. Types of Cyber Insurance Policies Cyber insurance is generally classified into two main types: First-Party Coverage Protects your organisation against direct losses such as: Third-Party Coverage Protects against claims made by others for damages due to: Businesses often require both types of coverage for full protection. How to Choose the Right Cyber Insurance Company When selecting a cyber insurance provider, consider: Top Cyber Security Insurance Companies in the US Here are some leading cyber security insurance companies dominating the US market: a) Chubb Renowned for its broad coverage options, including first and third-party policies, with strong breach response capabilities. b) AIG (American International Group) Offers comprehensive policies with high limits suitable for large enterprises and global operations. c) Travelers Provides extensive risk management resources to prevent cyber attacks, along with competitive premiums for SMEs. d) Hartford Known for policies tailored to small businesses with simple underwriting and quick claim settlement. e) Beazley A pioneer in cyber insurance, providing proactive breach response services that include legal, PR, and IT forensic experts. Leading Global Cyber Insurance Providers Apart from US providers, here are top global cyber insurance companies: a) AXA XL A global giant with strong cyber insurance solutions and innovative risk assessment tools. b) Zurich Insurance Group Offers tailored cyber policies for multinational corporations with cross-border coverage needs. c) Allianz Global Corporate & Specialty Provides dedicated cyber protection with strong emphasis on risk prevention and resilience. d) Sompo International Combines underwriting expertise with global incident response services. e) Munich Re One of the world’s largest reinsurers, offering robust cyber insurance backed by vast data analytics capabilities. Key Factors to Compare Cyber Insurers When evaluating cyber insurance companies, compare: Choosing an insurer that understands your business model and risks is crucial. Future of Cyber Security Insurance By 2030, experts predict that cyber insurance will evolve to include: Businesses will increasingly prioritise insurers offering proactive protection and AI-powered risk assessment. Conclusion As cyber threats grow in complexity and frequency, partnering with the right cyber security insurance company has become non-negotiable for businesses aiming for sustainable growth. Whether you’re a small business owner or leading a global enterprise, investing in comprehensive cyber insurance coverage ensures you remain resilient against financial, legal, and reputational losses. Remember: cyber insurance is not a substitute for strong cybersecurity practices but a critical layer in your risk management strategy.
Day Trading Rules: PDT, FIFO, Taxes & How to Trade Legally (2025 Guide)

Introduction to Day Trading Rules Considering entering day trading? Before you begin, you must know the exact regulations guiding this fast, risky trading approach. Simple words will help you to trade with assurance by splitting down every you must know.This guide focuses on U.S. rules—if you trade elsewhere (for example, India’s SEBI guidelines), check your local regulator. Day Trading: What is it? Overview and Definitions Buying and selling financial assets inside the same trading day defines day trading. Unlike investors who keep assets for months or years, day traders aim to benefit from short price swings. Day Trading versus Swing Trading: How They Differ? Capturing medium-term trends, swing trading usually keeps overnight positions for a few days to weeks. On the other hand, day trading ends all trades by the market closing, therefore avoiding overnight risks. Importance of Day Trading Regulations a. Viewpoints on Risk Management Rules keep dealers from destroying their accounts in one disastrous transaction. To make sure you’re not betting your whole portfolio on one concept, they help with entry, exit, and position sizing. b. Legal and Regulatory Expectations Regulatory agencies such the SEC and FINRA set regulations to safeguard investors against unneeded liabilities and dealers against excessive risk. Regulation for Pattern Day Traders (PDT)What then is the PDT Rule? Traders making four or more day trades within five business days must keep a minimum margin account equity of $25,000 according to the PDT rule. Dropping below this entails penalties. How to Avoid PDT Restraints One may prevent this by: Restricting transactions to fewer than four in five days. Utilizing a cash account (with T+2 settlement restrictions). Minimal Equity Requirements for Day Trading SEC and FINRA Standards FINRA demands that, in order to keep trading without limits, pattern day traders keep $25,000 in their accounts. This guarantees your margin trades have enough collateral for brokers. The 90-Day Restrictor Rule The 90-day Rule: Why? Your account might be frozen for 90 days or until the minimum equity requirement is met if you are flagged as a PDT and do not meet it. Undercapitalized traders are thereby stopped from overtrading. First In, First Out (FIFO) FIFO’s Influence on Your Trades In the US, FIFO calls first sold your oldest positions when partially departing assets. This affects capital gains computations and could make your tax reporting more difficult. The 3-Day Settlement Rule, T+2 Settlement Cycle Interpretation Two business days follow your selling of stocks before the money formally arrives in your account. This is especially important for cash accounts since you cannot recycle unresolved monies without breaking free-riding policies. Margin Account Conditions Cash account versus Margin account While margin accounts let you borrow from your broker, a cash account only permits settled cash for transactions. For flexibility, day traders usually choose margin accounts, however this has PDT requirements. Main Principles of Risk Management 1% Risk Rule These are best-practice guidelines, not regulations. Many traders choose the 1% rule: On a single trade, risk no more than 1% of your funds. Stop Loss and Take Profit Methodologies Setting stop losses safeguards your downside, whereas take profit targets guarantee you lock in profits without becoming avaricious and risking reversals. Mental Regulations for Day Trading Steering clear of overtrading Trading too frequently causes hasty judgments, thereby raising losses. Concentrate on good configurations rather than number. Gracefully Dealing with Losses Trading involves losses. Embrace them, examine your errors, and keep forward without retaliatory trading to swiftly recover losses. Day traders’ tax regulations Mark-to-Market Election under Section 475(f) This IRS rule allows active traders to handle profits and losses as regular income, so simplifying tax return and allowing deduction of limitless losses against other income. Wash Sale Rule This stops you from seeking tax deductions on a loss if you reacquire the same or nearly identical security within 30 days prior to or after the sale. Broker Specific Regulations Commissions and Account Minimums Minimum funding requirements and commission rates vary from one broker to another. Always read them to make certain they fit your trading technique and frequency. In Conclusion Day trading is much more than merely clicking buy and sell buttons all day. Under rigid guidelines and intelligent techniques, it is a game with organization. “Following these day trading rules helps you comply with the law and protect your capital from unnecessary risks.” Frequently Asked Questions What if I violate the PDT rule? For 90 days or until you reach the minimum equity requirement of $25,000, your broker will limit your account only to closing deals. Less than $25,000? Can I day trade? Yes, however in five business days you will be limited to less than four day trades or have to utilize a cash account in managing settlement restrictions. In the United States or India, is day trading unlawful? No, day trading is allowed in both nations provided you meet regulatory standards. Day trading’s 2% rule is what? This is a risk management approach whereby you risk no more than 2% of your capital on one transaction. Many favor the 1% rule for higher safety. In a day, how many transactions can a day trader execute? With a margin account over $25,000, there is no restriction. For cash accounts, your transactions follow your settled funds.
Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank: Strengthening Asia’s Economic Backbone

What is the Asian Infrastructure Investment Bank? Definition and Purpose of AIIB The AIIB is a multilateral bank created to fund infrastructure projects in Asia. Its goal is to help countries build better roads, clean energy, and water systems. It aims for sustainable growth, which means development that lasts and doesn’t harm the environment. The bank was founded in 2016 by China, with many other nations joining later. Its strategic focus is to support projects that improve lives and strengthen economic ties across the continent. Governance and Structure The AIIB is run by its members, which include countries from Asia and beyond. Each member has a say in decision-making, based on how much money they contribute. The bank operates with a clear set of rules — more like a club that works together rather than a single boss. Compared to large banks like the World Bank, AIIB focuses on projects suited specifically for Asian countries’ needs. Members vote on projects, ensuring transparency and shared responsibility. Funding and Capital Resources AIIB gets most of its money from member contributions and bond sales. These funds are used to finance big projects that can give long-term benefits. The bank also follows strict rules to ensure it stays financially healthy, avoiding risky investments. Its investments follow clear policies, prioritising social and environmental safety. In turn, this keeps projects sustainable and impactful for local communities. Formation and Objectives AIIB was proposed by China in 2013 to address the glaring infrastructure deficits across Asia. With its headquarters in Beijing, the bank began with 57 founding members, expanding to over 100 approved members worldwide within a few years. The bank’s core objectives are: Capital Structure and Voting Rights AIIB’s authorised capital stock is USD 100 billion, making it the second-largest multilateral development bank after the World Bank. Its capital is divided among members based on their economic size and GDP, with China as the largest shareholder holding approximately 26.5% voting rights, followed by India and Russia. Voting power is structured into: Strategic Goals and Key Areas of Investment Infrastructure Development Focus AIIB targets key sectors like energy, transport, water, and digital networks. Asia needs huge amounts of infrastructure; estimates suggest trillions of dollars are needed over the next decade. These investments aim to modernise cities, reduce travel time, and bring clean power to more homes. Projects like roads, bridges, and smart cities are high on the list. They make everyday life easier while boosting economic growth. Promoting Sustainable and Inclusive Growth Green energy is central to AIIB’s plan. Projects that promote solar, wind, and hydro power are essential for fighting climate change. The bank wants to help countries adapt to new climate realities and reduce reliance on fossil fuels. It also encourages inclusive growth — making sure the benefits reach everyone, including vulnerable groups. Implementing social and environmental safeguards means projects won’t harm nature or communities. Regional Connectivity and Economic Integration AIIB promotes projects that connect countries and communities. Better roads, railways, and ports help trade move faster and cheaper across borders. Examples include the Asian Highway Network and projects linked to China’s Belt and Road Initiative. These investments strengthen ties, encourage tourism, and create jobs. The goal is to make Asia more linked, so everyone benefits from shared growth. Key Projects Funded by AIIB India’s Infrastructure Expansion AIIB has provided substantial funding for India’s transport and energy sectors, including: Bangladesh Power System Upgrade A USD 404 million loan for upgrading power transmission networks to reduce losses and improve grid stability. Pakistan’s Hydropower Development The Tarbela 5 Hydropower Extension Project co-financed with the World Bank, enhancing energy security and renewable power generation capacity. Oman’s Duqm Port Development Supporting the construction of commercial terminals and infrastructure to transform Duqm into a major logistics and industrial hub in the Middle East. Indonesia’s Slum Upgrading Program Funding of USD 216.5 million to improve urban living conditions and water sanitation facilities in Indonesian cities. Global and Regional Influence of AIIB Role in Shaping Asian and Global Economic Policy AIIB influences how Asia funds projects, encouraging more responsible investments. Its focus on sustainability and regional development guides other institutions. It also works with international groups, sharing best practices and increasing effectiveness. Strategic Partnerships and Collaborations AIIB collaborates with countries like China, India, and Japan. It partners with ASEAN and other regional groups to promote infrastructure. Private companies and new finance tools—like green bonds—are also part of its strategy. These partnerships bring fresh ideas and funding sources. Challenges and Criticisms Some critics worry about political influence, especially since China is a major member. Environmental concerns also get raised over some projects. Transparency remains a challenge, but AIIB’s commitment to clear rules helps address these issues over time. AIIB vs Other Multilateral Banks Unlike traditional banks such as the World Bank and Asian Development Bank, AIIB focuses exclusively on infrastructure investment, maintains a non-resident board for efficiency, and adopts a project-based risk management model. Its fast-track approval process and lean operational framework attract both borrowing countries and private partners seeking agile financing solutions. Environmental and Social Safeguards AIIB integrates stringent environmental and social frameworks (ESF) into its project cycle to: Future Outlook and Strategic Initiatives Expansion Plans and New Investment Sectors AIIB plans to grow beyond traditional sectors. Digital infrastructure, renewable energy, and urban resilience are future targets. The bank also wants more countries to join and expand its reach across Asia. Innovation in Infrastructure Financing Using green bonds, blended finance, and public-private partnerships, AIIB looks to make funding more effective. Emerging tech like smart infrastructure, IoT (Internet of Things), can make projects smarter and more efficient, making investments last longer. Key Policy Recommendations for Stakeholders Recipient countries should focus on clear planning and transparency to get the most out of investments. Private investors can find new opportunities, especially in green projects and smart cities. Collaboration and openness will be key to success. Conclusion AIIB is transforming Asia’s infrastructure landscape, helping countries grow in smarter, greener ways. Its projects support economic progress, regional
Equity Trading: Comprehensive Guide to Strategies, Risks, and Opportunities

What is Equity Trading? Equity trading refers to the buying and selling of company shares in the stock market with the aim of generating profit from market price fluctuations. It involves ownership in a company where traders purchase stocks at lower prices and sell them at higher prices to earn capital gains. Institutional investors, retail traders, and mutual funds actively engage in equity trading to grow wealth, hedge risks, or manage portfolios. Types of Equity Trading 1. Intraday Trading Intraday trading involves buying and selling shares within the same trading day. Traders do not hold positions overnight, reducing exposure to after-market risks. It requires technical analysis, quick decision-making, and market trend understanding. 2. Delivery Trading In delivery trading, traders buy stocks and hold them beyond a single day, aiming for long-term capital appreciation. This type of trading does not involve leverage and is suitable for investors looking for dividends and company growth benefits. 3. Margin Trading Margin trading allows traders to buy more stocks than their available capital by borrowing funds from brokers. While it increases purchasing power, it also magnifies risks, making it suitable only for experienced traders. 4. Swing Trading Swing traders hold stocks for a few days to weeks, targeting short- to medium-term market swings. They utilise technical indicators, candlestick patterns, and market sentiment analysis to make decisions. 5. Arbitrage Trading Arbitrage trading involves buying a stock in one market and simultaneously selling it in another market at a higher price, capitalising on price discrepancies. This type requires speed, infrastructure, and capital to execute efficiently. Key Participants in Equity Trading Equity Trading Strategies 1. Fundamental Analysis Strategy This strategy involves analysing a company’s financial statements, balance sheet, cash flows, management quality, industry position, and economic factors to determine its true value. Investors buy undervalued stocks to gain long-term profits. 2. Technical Analysis Strategy Technical traders focus on price charts, trend lines, support and resistance levels, moving averages, and volume indicators to predict price movements and plan entry or exit points. 3. Momentum Trading Strategy Momentum traders buy stocks showing upward price momentum with high trading volumes and exit when momentum fades, aiming for quick profits within short timeframes. 4. Breakout Trading Strategy Breakout traders enter positions when stock prices move above resistance levels or below support levels with high volume, anticipating significant price moves post-breakout. 5. Scalping Strategy Scalpers make multiple trades within minutes or seconds, profiting from minor price fluctuations. This demands high concentration, advanced trading platforms, and minimal transaction costs. Risks Associated with Equity Trading 1. Market Risk Price fluctuations due to macroeconomic conditions, political events, or company-specific news can lead to losses. 2. Liquidity Risk Certain stocks may have low trading volumes, making it difficult to exit positions without impacting price. 3. Leverage Risk Using margin magnifies both profits and losses, potentially wiping out capital quickly. 4. Execution Risk Delays in order execution can cause traders to miss intended entry or exit prices, especially during high volatility. Benefits of Equity Trading Important Tips for Successful Equity Trading 1. Define Goals and Risk Appetite Establish clear investment objectives and risk tolerance before starting equity trading to align strategies with personal financial goals. 2. Diversify Portfolio Diversification across different sectors, industries, and market capitalisations minimises risk. 3. Stay Updated with Market News Follow economic data releases, earnings reports, central bank policies, and geopolitical events to make informed trading decisions. 4. Use Stop-Loss Orders Stop-loss orders limit losses by automatically selling a stock if it falls below a specified price, protecting capital in volatile markets. 5. Avoid Emotional Trading Trading decisions driven by fear or greed often lead to losses. Stick to strategy and maintain discipline. Technological Trends in Equity Trading 1. Algorithmic Trading Algorithmic trading utilises automated systems to execute trades based on pre-defined rules and market conditions. It ensures speed, accuracy, and efficiency, dominating modern trading floors. 2. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning AI models analyse vast market data to identify trading opportunities, predict market trends, and optimise portfolio management with minimal human intervention. 3. Mobile Trading Platforms Advanced mobile apps enable traders to monitor markets, analyse charts, and execute trades anytime, anywhere, increasing participation and liquidity. Regulatory Framework in Equity Trading In India, equity trading is regulated by SEBI (Securities and Exchange Board of India) ensuring transparency and protecting investor interests. In the USA, SEC (Securities and Exchange Commission) oversees equity markets. Regulations include insider trading restrictions, margin rules, circuit breakers, and disclosure norms. Conclusion Equity trading offers immense opportunities for wealth creation, portfolio diversification, and passive income generation. However, it demands a deep understanding of markets, disciplined strategy implementation, risk management skills, and emotional stability. With advancing technology, increased access to data, and evolving trading platforms, traders can leverage tools to enhance profitability while mitigating risks effectively. Here is some books where you can master the investing more (investing books)